CLASS 10 UNIT 3 SESSION 3: PERFORM OPERATIONS ON TABLE IMPORTANT NOTES
CLASS 10 UNIT 3 SESSION 3: PERFORM OPERATIONS ON TABLE IMPORTANT NOTES
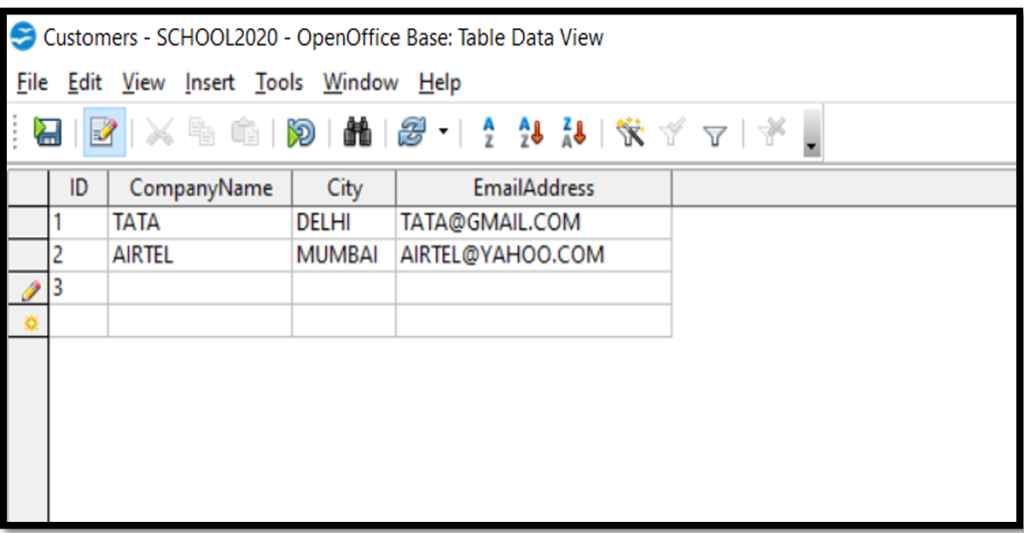
Inserting Data In The Table:
Select the table > Double click on it.
The table will open in Datasheet View in which data new data can be inserted and existing
data can be updated or removed.
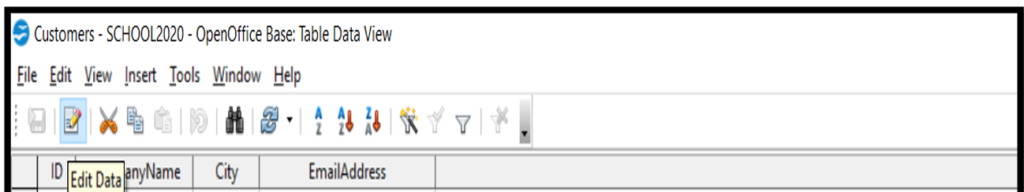
Editing Records In The Table:
To edit the data either click on edit icon or double on the data in the cell of a table and modifications can be done.
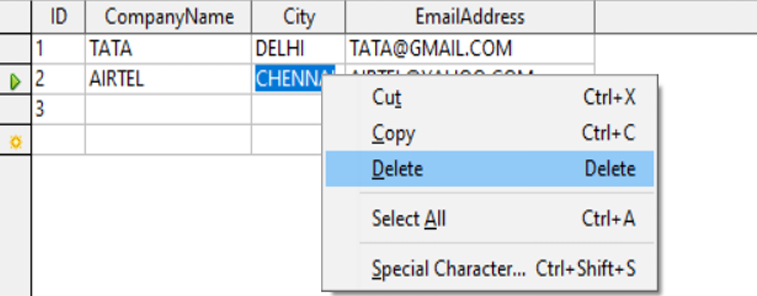
Deleting Records From The Table:
Select the data > right click on selected data > select the Delete option.
Field Properties:
To set the field properties, steps will be followed as:
Select the table > Right click > Select the option Edit > the table Design View window will open.
In design view there are different properties of fields according to the data type set for each field.
The properties of numeric type data is shown below in the figure.
AutoValue – if set to yes then field will get the auto numeric values.
Length – By default length of the field is 10 but the size of the field can be set to maximum length.
Default Value – A default value can be set for a field if user don’t provide any value while entering the values in the table.
Format example – This property helps to set the format of the data entered in the field such as 91-222-333.
The properties of character type data is shown below in the figure.
Entry Required – if set to yes then it will be must to insert the value in the field which
means that field cannot be left blank.
Length – By default length of the field is 10 but the size of the field can be set to
maximum length.
Default Value – A default value can be set for a field if user don’t provide any value
while entering the values in the table.
Format example – This property helps to set the format of the data entered in the field
such as 91-222-333.
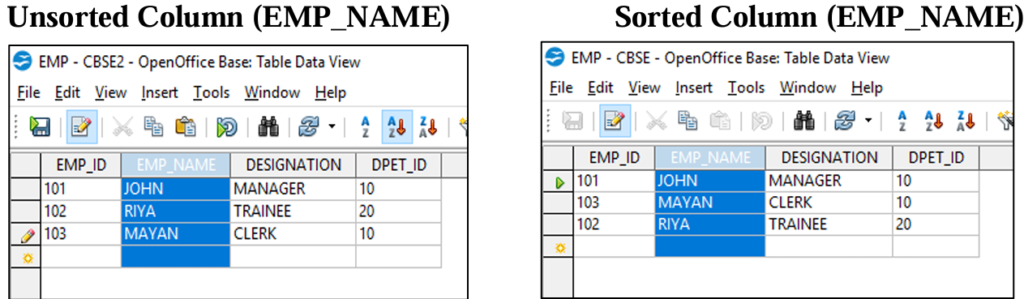
Sorting Data:
Sorting means to arrange the data in either ascending order of descending order. Select the column(s) then click on sort buttons.
Referential Integrity:
Referential integrity is used to maintain accuracy and consistency of data in a relationship.
Referential integrity helps to avoid:
1.Adding records to a related table if there is no associated record available in the primary key table.
2.Changing values in a primary if any dependent records are present in associated table(s).
3.Deleting records from a primary key table if there are any matching related records available in associated table(s).
Creating and Editing Relationships between Tables:
A relationship refers to an association or connection between two or more tables. When you relate two tables, you don’t need to enter the same data in separate tables.
Relationships between tables helps to:
Save time as there is no need to enter the same data in separate tables.
Reduce data-entry errors.
Summarize data from related tables.
There are three types of relationships which can be created in tables:
- ONE to ONE
- ONE to MANY OR MANY to ONE
- MANY to MANY
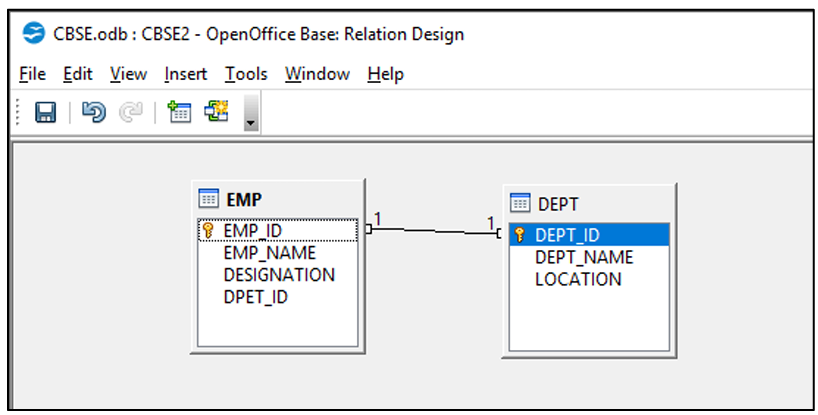
One to One Relationship:
In this relationship, both the tables must have primary key columns. Example: In the given tables EMP and DEPT, EMP_ID in EMP table and DEPT_ID in DEPT table are the primary keys.
One to Many Relationship:
In this relationship, one of the table must have primary key column. It signifies that one column of primary key table is associated with all the columns of associated table.
Many to Many Relationship:
In this relationship, no table has the primary key column. It signifies that all the columns of primary key table are associated with all the columns of associated table.
Remove the Relationships:
The relationships applied on the tables can be removed also with the help of Delete option.
Right Click on the relationship thread and select Delete option.
2 thoughts on “CLASS 10 UNIT 3 SESSION 3: PERFORM OPERATIONS ON TABLE IMPORTANT NOTES”