Unit-1 BASICS OF NETWORKING AND WEB ARCHITECTURE Important questions
Unit-1 BASICS OF NETWORKING AND WEB ARCHITECTURE Important questions
Fill in the blanks:
a. Two or more computers connected to each other for information exchange form a __________.
Answer: Network
b. The range of frequencies available for transmission of data is called____________.
Answer: Bandwidth.
c. __________ is the network of networks.
Answer: The Internet
d. A technique in which a dedicated and complete physical connection is established between two nodes for communication is ________switching.
Answer: Circuit Switching
e. Any computer attached on the network is called a ______.
Answer: Nodes of the network.
Multiple Choice Questions:
1) Choose the option, which is not included in networking.
a. Access to remote database
b. Resource sharing
c. Power transferring
d. Communication
Answer: c. Power transferring
2) Data transfer rate is often measured in
a. Mbps
b. Kbps
c. Bps
d. gbps
Answer: c. Bps
3) Which one of the following is not in the category of communication channels?
a. narrow band
b. broadband
c. light band
d. voice band
Answer: c. light band
4) The greater the bandwidth of a given medium, the __ is the data transfer rate
a. higher
b. lower
c. both a and b
d. neither a nor b
Answer: a. higher
5) What is the approximate bandwidth of a typical voice signal?
a. 2KHz
b. 2MHz
c. 3KHz
d. 3MHz
Answer: c 3KHz
Unit-1 BASICS OF NETWORKING AND WEB ARCHITECTURE Important questions(Exercise)
3.Expand the following:
a. ARPANET. :Advanced Research Projects Agency NET.
b. DTR : data transfer rate
c. NIU : network interface unit
d. ISP : Internet Service Provider
e. FTP : File Transfer Protocol
f. TCP : Transmission Control Protocol
g. SMTP : Simple Mail Transfer Protocol
h. VoIP : Voice over Internet Protocol
Unit-1 BASICS OF NETWORKING AND WEB ARCHITECTURE Important questions
LONG ANSWERS:
1.What is a network? Give any two uses of having a network in your school computer lab.
Answer: A network is any collection of independent computers that communicate with one another over a shared network medium. A network allows sharing of files, data, and other types of information giving authorized users the ability to access information stored on other computers on the network.
2. Mention any two disadvantages of a network.
Answer: 1.If the file server breaks down, the files on the file server become inaccessible.
2. Virus can spread to other computers throughout a computer network.
3. What are the requirements for setting up a network?
Answer: Every network includes:
● At least two computers – Server or Client workstation.
● Network Interface Cards (NIC) A connection medium, usually a wire or cable, although wireless communication between networked computers and peripherals is also possible.
● Network Operating system software, such as Microsoft Windows NT or 2000,Unix and Linux.
4. How is a dedicated server different from a non dedicated server?
Answer: Dedicated server is the one which can help the client’s workstations to just have properly authorized access request associating to software, hardware whereas, a non dedicated server permits to utilize itself as a workstation as well as gives the facility of sharing the resources with other computers on the internet.
5. Define a channel. Name the three categories of communication channels.
Answer: Channel: A communication channel is a medium that is used in the transmission of a message from one point to another. we can say that it is a pathway over which data is transferred between remote devices.
We have three broad categories of communication channels –
1.Narrow band which is slow and used for telegraph lines and low speed terminals;
2. Voice band used for ordinary telephone communication
3. Broadband which is fastest and is used for transmitting large volumes of data at high speeds.
6. What do you mean by bandwidth and DTR?
Answer: Bandwidth: Bandwidth refers to the range of frequencies available for transmission of data. It is expressed as the difference in Hertz(Hz) between the highest frequency and the lowest frequency. Wider the bandwidth of a communication system, greater is the capacity and hence greater is the amount of data that can be transmitted over a period of time.
DTR: (DTR) is the amount of data in digital form that is moved from one place to another in a given time on a network. The greater the bandwidth of a given medium, the higher is the data transfer rate. Data transfer rate is often measured in bits per second (bps).
7.Two companies in different states wanted to transfer information. Which type of network will be used to implement the same?
Answer: WAN
8. Two schools in the same city wanted to transfer e-learning information. Which type of network will be used to implement the same?
Answer: Metropolitan Area Network (MAN)
9.Two teachers in the same school sitting in different labs wanted to transfer information. Which type of network will be used to implement the same?
Answer: Local Area networks (LAN)
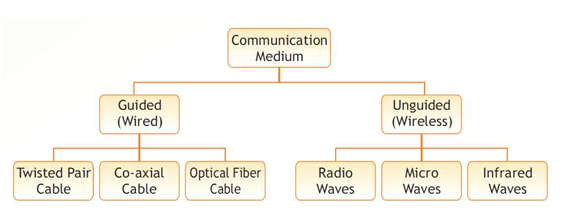
10. What do you mean by a transmission medium? Differentiate between guided and unguided transmission media.
Answer: A transmission medium refers to the channel of transmission through which data transmitted from one node to another in the form of signal. A transmission medium may belong to of the following two categories:
● Guided Medium: The term refers to physical conductors such as twisted pairs, coaxial cable, and fiber optics. In twisted pair and coaxial cable, the signal travels as voltage and current signal whereas in optical fibre, light.
● Unguided Medium: The unguided medium uses electro not require a physical conductor. Examples of unguided medium include microwave, radio wave, infrared.
11.Define the term topology.
Answer: The arrangement (also called layout) of nodes in a network is called network topology. There are broadly two types of topologies: broadcast and point to point
12. List any two advantages and any two disadvantages of Star topology.
Answer: Advantages:
- It is very reliable – if one cable or device fails then all the others will still work
- It is high-performing as no data collisions can occur
- Less expensive because each device only need one I/O port and wishes to be connected with hub with one link.
- Easier to put in
Disadvantages:
- Requires more cable than a linear bus .
- If the connecting network device (network switch) fails, nodes attached are disabled and can’t participate in network communication.
- More expensive than linear bus topology due to the value of the connecting devices (network switches)
- If hub goes down everything goes down, none of the devices can work without hub.
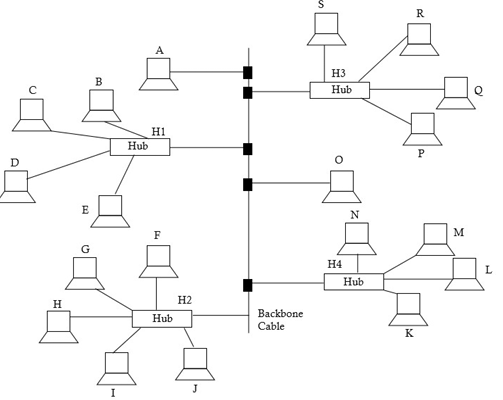
13. How is Tree Topology different from Bus topology?
Answer:
● Tree Topology
tree topology is a hybrid topology using a combination of star and bus topology. Backbone cable in a bus topology acts like the stem of the tree, and star networks are connected to the main tree topology is a hybrid topology using a combination of star and bus topology. Backbone cable in a bus topology acts like the stem of the tree, and star networks (and even individual nodes) are connected to the main backbone cable like the branches of
tree.
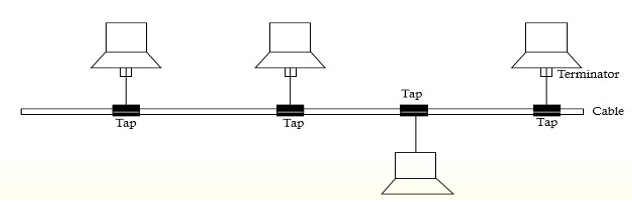
● Bus Topology
In bus topology, there is a long cable, called backbone cable (or simply backbone), that connects various nodes through a connector called tap. In this, a message sent by one is received by all devices connected to backbone cable. This
topology requires less cabling and is easy to install and extend the network laid using it. however, fault detection and isolation is difficult.
14.Identify the type of topology from the following.
a. Each node is connected with the help of a single cable.
b. Each node is connected with the help of independent cable with central switching.
Answer:
a. Bus topology
b. Star topology
15. Ms. Anjali discovered that the communication between her centre and the primary block of the school is extremely slow and signals drop quite frequently. The distance between these two blocks is 140 meters.
a. Name the type of network.
b. Name the device which may be used for smooth communication.
Answer:
a. Local Area Network
b. Repeater
16. ABC International School is planning to connect all computers, each spread over a distance of 50 meters. Suggest an economic cable type having high speed data transfer to connect these computers.
Answer: Optical Fiber cable
17. Sahil wants to transfer data across two continents at very high speed. Write the name of the transmission medium that can be used to do the same. Write the type of network also.
Answer: transmission medium is Fiber optical cable. Type of network is WAN.
18. Mayank wants to transfer data within a city at very high speed. Write the name of the wired transmission medium that he should use. Write the type of network also.
Answer: Wired transmission medium – Optical fiber cable Type of network – MAN.
19. Mr. Akash wants to send/receive email through the internet. Which protocol will be used for this purpose?
Answer: SMTP Protocol(Simple Mail Transfer Protocol)
20. Answer the following questions in the context of a computer lab with 100 computers.
a. Which device is used to connect all computers inside the lab?
b. Which device is used to connect all computers to the internet using telephone wire?
Answer:
a. Hub or Switch
b. Modem
21. Name the device that establishes an intelligent connection between a local network and external network with completely different structures.
Answer: Gateway establishes an intelligent connection between a local network and external network with completely different structures.
22.Name the network device that works like a bridge to establish connection between two networks but it can also handle networks with different protocols.
Answer: Gateway
23.Neha wants to upload and download files from/to a remote internal server. Write the name of the
relevant communication protocol, which will let her do the same.
Answer: FTP (File Transfer Protocol)
24. Meha wants to upload hypertext documents on the internet. Write the name of protocol, which will let her do the same.
Answer: HTTP is used to upload hypertext documents on the internet.
25. This protocol is used for communication between two personal computers using a serial interface and connected by a phone line. Write the name of the protocol.
Answer: PPP (Point-to-Point Protocol) is a protocol for communication between two computers using a serial interface, typically a personal computer using a MODEM connected by phone line to a server.
26. This protocol is used to transfer email over the internet. What is the name of the protocol?
Answer: The Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP) is used to deliver e-mail messages over the Internet. This protocol is used by most e-mail clients to deliver messages to the server, and is also used by servers to forward messages to their final destination.
27. This protocol is used to implement remote login. What is the name of the protocol?
Answer: Telnet is used to implement remote login.
28. This protocol is used for chatting between two groups or between two individuals. Write the name of the protocol.
Answer: IRC (Internet Relay Chat) is used for chatting between two groups or between two individuals
29. This protocol is used to transfer voice using packet switched networks. Write the name of the protocol.
Answer: Voice over Internet protocol (VoIP) is used to transfer voice using packet switched networks.
30. Explain Remote Access Protocol.
Answer: A remote access protocol is responsible for managing the connection between a remote access server and a remote computer. PPP is a remote access protocol that allows you to implement TCP/IP. It creates a connection with a remote machine.
31. Why do we need VoIP protocol?
Answer: Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP), is a technology that allowing you to make voice calls over a broadband Internet connection instead of an analog (regular) phone line. Some VoIP services offer features and services that are not available with a traditional phone. It provide smoother connection than an analog signal.
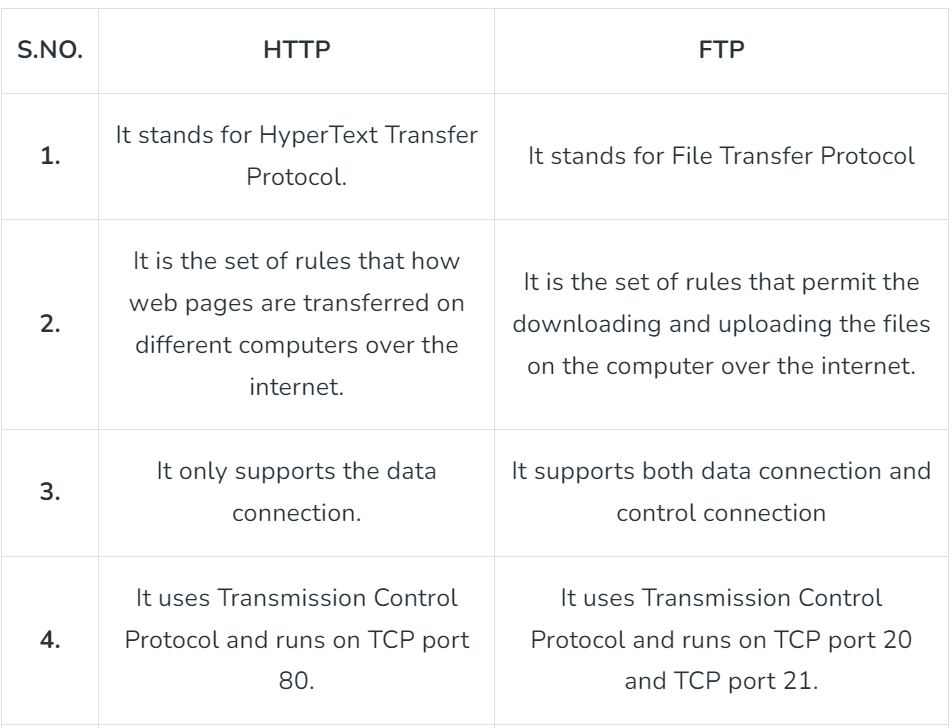
32. Differentiate between FTP and HTTP.
Answer:
33. Differentiate between VoIP and IRC.
Answer: Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP), is a technology that allowing you to make voice calls over a broadband Internet connection instead of an analog (regular) phone line. It is cheaper than analog call. While IRC (Internet Relay Chat) is used for chatting between two groups or between two individuals
34. Explain the three types of web architecture
Answer:
Web Architecture can be defined as the conceptual structure of the internet. The WWW or internet is a constantly changing medium that enables communication between different users and the technical interaction between different systems and subsystems.
Types of web architectures
I) Client-server model: Initially, the web consisted of a two-tiered architecture: clients and servers. Clients and servers shared the tasks and services that the system was supposed to perform. Example: Web Server.
II) Three-tier model: Three-tier models include an application logic between the client and the server, which handles the data processing and allows a certain degree of interaction. For example, an application server can process data while a database server is dedicated solely to data storage.
III) Service-oriented architectures (SOA): With SOAs, business processes can be automated by the involved systems communicating with one another – partly without human intervention – and performing certain tasks. Examples include online banking, e-commerce, e-learning etc.
35. Differentiate between IP address and MAC address
Answer: The primary distinction between MAC and IP addresses is that MAC addresses are used to verify the computer’s physical address. It uniquely identifies the network’s devices. While IP addresses are used to uniquely identify a device’s network connection.
36.Differentiate between Worm and Virus
Answer:
Virus: A virus is a software code that may harm your system by overwriting or corrupting the system files. A computer virus may make several copies of it by inserting its code onto the system programs and thereby may corrupt them. This causes the system to slow down or even stop functioning.
Worm: A worm is often received via network, and it automatically keeps on creating several copies of itself on the hard disk thereby flooding the hard disk. When a worm is received as an email attachment, it is automatically forwarded to the recipients leading to network congestion. Thus a worm may crash the system and entire network. No host application is required for worms to replicate themselves.
37.Explain the significance of the IT Act.
Answer:
An amendment in IT Act 2000 named Information Technology Amendment Act,2008 was also introduced. The act also defines offences and penalties for cyber-crime. Cyber police are responsible for detecting such crimes and taking the necessary measure against it according to the IT Act.
Cyber offences under IT Act
● Tampering with computer source documents – Section 65
● Hacking -Section 66
● Publishing of information which is obscene in electronic form -Section 67
38. Explain the following terms: Patent Copyright Trademark
Answer:
Patent: Patent is a term used for a specific product designed by an individual. The designer is given exclusive rights over the patent for a limited period of time. With help of the patent right, the owner can stop others from making, using or selling the product design. The owner can take a legal action if someone uses the patent without his/ her permission.
Trademark: Trademark can be defined as a name or a different sign or a device identifying a product or a service. The product or the service is produced or provided by a specific person or a company. A Trademark is also known as brand name. It should be officially registered and legally restricted to the use of the specific person or the company.
Copyright: Copyright is the term used for a written document. A legal action can be taken, if copyrights are violated. The following category of work can be considered for copyrights. literary works musical works, including any accompanying words
39. Differentiate between hacking and cracking
Answer: Hacking: Hackers are good people who hack devices and systems with good intentions. They might hack a system for a specified purpose or for obtaining more knowledge out of it. The term was used for people who engaged themselves in harmless technical experiments and fun learning activities.
Cracking: Crackers are people who hack a system by breaking into it and violating it with some bad intentions. They may hack a system remotely for stealing the contained data or for harming it permanently.
40. Rohan wants to prevent unauthorized access to/from his company’s local area network. Write the name of the system, which he should install to do the same.
Answer: Rohan should install Firewall.
41. When the user browses a website, the web server sends a text file to the web browser. What is the name of this?
Answer:
When the user browses a website, the web server sends a text file to the web browser in the form of cookies.
42. It is defined as a crime in which a computer and internet is used in an illegitimate way to harm the user. What is the name of this crime?
Answer: Cybercrime.
43. A person who gains unauthorized access to a computer with the intention of causing damage. What is the name of this crime?
Answer: Hackers.
One thought on “Unit-1 BASICS OF NETWORKING AND WEB ARCHITECTURE Important questions”